|
 Length
and time Length
and time
- What is the SI unit of length?
meter (m)
- What is the SI unit for time?
second (s)
 Distance and
Displacement Distance and
Displacement
- Compare between distance and displacement.
- Distance and displacement
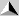
are different. When you traveled 50 km to the East and then 20 km to the
West, the total distance you traveled is 70 km, but your displacement is
30 km East.
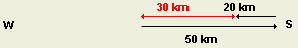
- Displacement is the length of the shortest path directed from the
initial point to the final point.
- Distance is the total length of all paths that link the initial and
final points.
- In physics, we say that distance is a scalar
and displacement is a vector.
- Scalar has a magnitude and vector has both a magnitude and a
direction.
- Scalar is one dimensional and vector is two dimensional.
- What is the relation distance speed and
displacement?
If the object is moving in a straight line without reversing its
direction, then distance is equal to magnitude of displacement .
However, if the object is reversing its direction the distance is not equal
to magnitude of displacement.
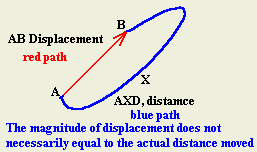
- An object moved on rectangular path as
shown. It started from A, passing through B, C and stopped at D.
Find the followings:
1- What is the distance traveled?
Distance=10+5+10=25m (path ABCD)
2- What is the displacement of the object?
Displacement=5=5m (path AD)
|
 |
A car moved 50 km to the North. What is its displacement?
50 Km north
A car
moved 20 km East and 70 km West. What is the distance? 90 Km
How do we evaluate displacement? Displacement=S=Sf-Si
where Si is the initial distance and Sf is the final
distance.
 Average,
speed and
Instantaneous Velocity Average,
speed and
Instantaneous Velocity
- What is velocity?
Velocity is
defined as the rate change of displacement and it shows
how fast an object is moving and to which direction.
- What is meant by average velocity?
Average velocity can be
calculated by dividing displacement over time.
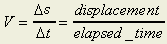
For example, when a car moved 50 km in 2 hours, the average velocity is 25.5
km/h because 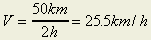 . .
- What is meant by speed velocity?
Speed is distance divided by time.
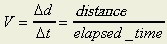
For example, when a car moved 50 km in 2 hours, the average speed 25.5
km/h because 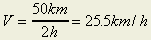 . .
- What is the relation between speed and velocity?
If the object is moving in a straight line without reversing its
direction, then speed is equal to the magnitude of the velocity.
However, if the object is reversing its direction the speed is not equal to
magnitude of velocity.
However, for all kind of motions the instantaneous speed is equal to the
magnitude of the instantaneous velocity.
- How do we evaluate displacement? Displacement=DS=Sf-Si
- How do we evaluate elapsed time ? elapsed
time=Dt=tf-ti
- What is meant by instantaneous velocity ?
The instantaneous velocity
shows the velocity of an object at one point in time. For example, when you are
driving a car and its speedometer swings to 90 km/h, then the instantaneous
velocity of the car is 90 km/h.
- Why the instantaneous
velocity is not always equal to
average velocity? Because instantaneous velocity is taken at one
point in time while average velocity is taken at an interval of time.
- A car moved 20 km East and 60 km West in 2 hours.
What is its average velocity?
V=Displacement/time=(60-20)/2=20 km/h
- How far will a car travel in 15 min at 20 m/s?
v=d/t, d=v t= 20x15x60=18000m=18 km.
-
A car travels 600 m in 30 s. What is its average
speed? v=d/t=600/30=20.
-
An object moved on rectangular path as shown. It
started from A, passing through B, C and stopped at D within 10 seconds.
Find the followings:
1- What is the speed of the object ?
Speed=distance/time=(10+5+10)/10=2.5m
(path ABCD)
2- What is the velocity of the object if it took
2 seconds to move the AD path? Velocity=Displacement/time=5/2=2.5
m/s |
 |
 Acceleration Acceleration
- What is acceleration?
When an object's velocity changes, it accelerates. Acceleration
shows the change in velocity in a unit time. Velocity is measured in meters
per second, m/s, so acceleration is measured in (m/s)/s, or m/s2,
which can be both positive and negative.
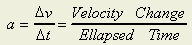
- What is meant by Average Acceleration? The average acceleration is the ratio
between the change in velocity and the time interval. For example, if a car moves from the rest to 5 m/s in 5 seconds, its
average acceleration is

- What is meant by Instantaneous Acceleration
An instantaneous acceleration
is the change in velocity at one moment. We will study instantaneous
acceleration more in depth later in the chapter.
- If a car accelerates from 5
m/s to 15 m/s in 2 seconds, what is the car's average acceleration? a=DV/Dt=Vf-Vi/tf-ti=(15-5)/2=5
m/s2
- How long does it take to
accelerate an object from rest to 10 m/s if the acceleration was 2 m/s2?
a=DV/Dt,
2=10/t, t=5 seconds
- Carl started to run at 10
km/h when he left his house. He arrived at school 30 minutes later. How fast
was he running when he arrived there? Assume that his average acceleration
was 30 km/h2. a=DV/Dt,
30=(Vf-10)/0.5h, 30*0.5=(Vf-10), Vf=15+10=25
km/h. Note 30 minutes=0.5 hour.
 Equations
of Uniform Motion (Constant Acceleration) Equations
of Uniform Motion (Constant Acceleration)
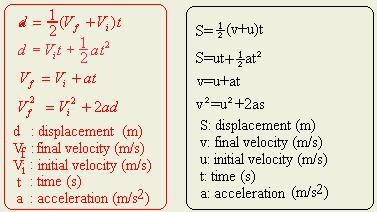
- List the four major equations of uniform motion
.
- Constant acceleration graph.
- If a car accelerated from 5
m/s to 25 m/s in 10 seconds, how far will it travel?
s=(u+v)t/2=(5+25)*10/2=30*10/2=150m.
- What is the displacement of
a car whose initial velocity is 5 m/s and then accelerated 2 m/s2
for 10 seconds?
S=ut+˝at2=5*10+0.5*2*102=50+100=150m
- What is the final velocity
of a car that accelerated 10 m/s2 from rest and traveled 180m?
V2=u2+2ad=zero2+2*10*180, v2=3600,
so v=60 m/s.
- Who studied falling objects?
Galileo was the first to find out that all objects falling to Earth have a
constant acceleration of 9.80 m/s2 regardless of their
mass.
- Explain the falling process of two object with
different masses?
When all object fall they have the same acceleration. Thus, if
we ignore the air resistance, the two objects reach the ground surface at
the same time regardless of their masses will .
- What is the value of acceleration due to gravity
"g" ? it is equal to 9.80 m/s2.
Therefore, if you drop a pen, it should behave like this
| Time (s) |
Velocity (m/s) |
Displacement (m) |
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
| 1 |
9.8 |
4.9 |
| 2 |
19.6 |
19.6 |
| 3 |
29.4 |
44.1 |
| 4 |
39.2 |
78.4 |
List the equations of motion for gravitational
acceleration.
For all uniform-motion equations, we can substitute g for a:


 How long will it take for an
apple falling from a 29.4m-tall tree to hit the ground?
How long will it take for an
apple falling from a 29.4m-tall tree to hit the ground?
s=ut+˝gt2,
29.4=zero*t+˝ 9.8 t2 , t2=2*29.4/9.8=6, t=2.45
seconds.
- What is mass?
Mass is a measure of an object resistance to motion
- What is weight?
Weight is the gravitational force exerted on an object by Earth.
- What are the differences between mass and weight
Mass and weight are different
in physics.
1- Mass doesn't change when you go to the Moon, but weight does.
2- Mass is a scalar quantity, but weight is a vector quantity that reflects
the size of gravity.
3- Mass is measured by Kilogram (Kg) but weight is measured by Newton (N).
- How do we calculate weight?
Weight is defined as mass times gravitational acceleration that is W
= mg where: W is weight in Newton (N), m is mass in kg, and g is the
acceleration of gravity in m/s2.
- If your mass is 70 kg on Earth, your weight is
W=(70 kg)(9.8 m/s2) = 686 N.
- What is the mass of an object that has a weight of
115 N on the Moon?
The gravity of the Moon is 1/6 of g (which is 9.8 m/s2).
 Test Yourself Test Yourself
- If you move 10 km North, 10 km East, and 10 km South
The below graph represents the position of a mouse at a
given time.
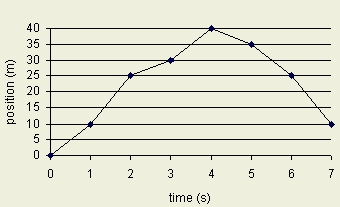
Answer the questions using the following graph.

1- What is the distance it traveled between t = 0 to
t = 2?
2- What is the instantaneous velocity when t = 4?
How long does it take for a car to
change its velocity from 10 m/s to 25 m/s if the acceleration is 5 m/s2?
A rat and a cat is
35 m apart. When the rat started to run at 2 km/h (0.556 m/s), the cat
started to chase him at 1 m/s2. Can the cat catch the rat in 10
seconds?
A car has a
constant acceleration of 4 m/s2, starting from rest.
a. How fast is
it traveling after 5 seconds?
b. How far is it
traveling after 5 seconds?
c. How far has
it traveled by the time it reached the speed of 40 m/s?
A car is at
velocity of 20 km/h. If the car traveled 120 km in 3 hours at constant
acceleration, what is its final velocity?
A car travels at
constant acceleration of 5 m/s2 from rest. How far has it
traveled by the time it reached the velocity of 72 km/h (20 m/s)?
How long will it
take for a falling object to reach 108 m/s if its initial velocity is 10
m/s?
What is the final
velocity of an apple if it falls from a 100m-tree?
|

