|
|
|
|
2.2.b Measurement of temperatureTemperatures
Thermometers
Celsius Scale
|
| It is made by joining two different metals assembled (e.g. copper& iron) into two junctions. One junction is placed in pure melting ice (Cold junction) and the other junction is placed in the hot object (called hot junction). | 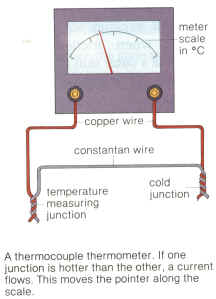 |

|
Describe the operation of a
thermocouple meter?
When there a difference in temperature between the hot and cold
junctions an electric current is generated. This current is used to
deflect a galvanometer which is calibrated to temperature degrees.
List the advantages of a thermocouple thermometer?
Easy to read by using a pointer or a digital display.
Scale can be placed a way from the temperature detector
Can be used automatic electrical control circuits.
Wide range of temperature -200°C to 1600°C
It has has a small thermal capacity and is used to measure rapidly changing temperatures.
List three precautions a person must take when measuring temperature?
Mercury thread should be kept along the scale the parallax errors
Line of sight should be perpendicular to scale.
Reading should be at the top of mercury thread.
1- Why Mercury or alcohol thermometers are
not suitable to measure temperatures deep inside a furnace?

For more information write: abumsamh@emirates.net.ae |