| 2 |
Thermal Physics
|
Where to go! |
| 2.1 |
Simple
Kinetic Molecular Modal of Matter
|
|
D
|
Pressure Changes
|
|
| Core-1 |
Relate the changes in volume
of a gas to change in pressure applied to the gas at constant temperature |
See Expansion |
| Sup-1 |
Recall and use the equation pV=constant
at constant temperature |
|
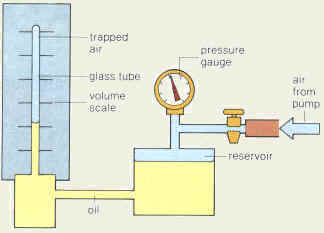
2.1.d Pressure changes at constant temperature
-
What is the relation between gas pressure and
volume at constant temperature?
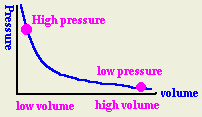
The relation is an inverse one. When volume is decreased,
pressure is increased and when volume is increased pressure is decreased. This can be written as V1P1=V2P2=constant
-
State Boyle's law.
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to
the pressure, if the temperature is constant
-
Explain the relation between pressure and volume using molecular theory?
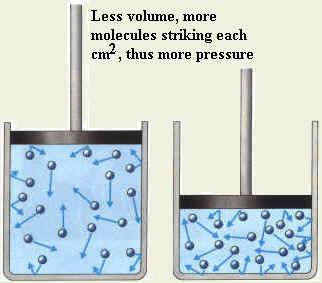
| If the volume of the gas is decreased, the molecules are crowded
in a smaller space and the area of the walls decreases then the number of
bombardments per second on the walls increases and the gas pressure
increase. |
 |
Explain how gases produce pressure on the walls
of their containers?
Gas molecules are in a state of continuous motion in all
directions, and they are constantly bombarding the walls of the
container. When the molecules bounce off the walls, they produce an outward
force on the walls which causes the outward pressure of the gas on
the walls of the container.
Explain how temperature increase the pressure of gases?
When the temperature rises, the gas molecules gain kinetic energy
and move faster and thus strike the container wall more frequently and with
greater force. Therefore, the total force exerted per unit area of the
walls is greater and the pressure increase.
|