| 2 |
Thermal Physics
|
Where to go! |
| 2.2 |
Thermal Properties
|
|
D
|
Melting and Boiling
|
|
| Core-1 |
Describe melting and boiling
in terms of energy input without a change in temperature |
|
| Core-2 |
State the meaning of melting
point and boiling point |
|
| Core-3 |
Describe condensation and
solidification |
|
| Sup-1 |
Distinguish between boiling
and evaporation |
|
| Sup-2 |
Use the term latent heat and
give a molecular interpretation of latent heat |
|
| Sup-3 |
Describe an experiment to
measure specific latent heats for steam and for ice |
|
Melting Point
- What is meant by melting point?
When a pure solid is heated, its temperature rises until it reaches the "milting point" where it remains constant until all solid changes to liquid.
- What is meant by "latent heat of fusion"?
Latent heat of fusion is the heat energy needed to change an abject from a solid state to a liquid state.
Latent heat of fusion is the energy needed to overcome the intermolecular force to separate the molecules during the melting process.
- Why it is called "Latent heat"?
Because it does not raise the temperature during absorption.
- Explain why latent heat of fusion does not increase the object temperature by the molecular theory?
The latent heat if fusion is the energy needed to overcome the intermolecular force to separate the molecules during the melting process. The absorbed energy causes the molecules to move further apart increasing their potential energy rather than kinetic energy. So, the kinetic energy does not change and so the temperature stays the same.
- What is meant by "Specific latent heat of fusion Lf"?
Specific latent heat of fusion Lf is the thermal energy required to change 1Kg of a solid to a liquid without a change in temperature.
- What is the amount of energy needed to change "m" kg from solid state to liquid state?
E=m Lf where
"m": mass in Kg
"Lf" is the latent heat of fusion
- How much heat is needed to change 0.2 kg of ice into water? E=m Lf =0.2*334000 =66800J.
- What is the difference between boiling and evaporation?
- Boiling occurs at a definite temperature (the boiling point), but evaporation occurs at all temperatures.
- Boiling occurs within all the volume of the liquid, but evaporation occurs at the surface of the liquid.
- In boiling, bubbles appear within the liquid, but there are no bubbles in evaporation.
- Describe an experiment to measure the specific latent heat of ice.
- Place an electric heater in the melting ice packed in a funnel.
- Switch on the heater and turn on the stop-watch and collect the water from melting the ice fir several minutes
- Switch off the heater and turn off the stop-watch and then find the mass "m" of collected water
- Apply the conservation of energy. The energy supplied by the heater equals the heat used to melt the ice
- P*t=m*Lf from which Lf=P*t/m where Lf is measured in "J/Kg"
- In this experiment where it is done at room temperature, ice will absorb heat from the surroundings and the collected water becomes greater than it should and thus the value of Lf obtained is smaller than the true value.
- Describe an experiment to measure the specific latent heat of steam.
- When the water is boiling take a reading for the mass by balance and recorded as "m1" and start stop-watch.
- After several minutes, stop the stop-watch and take another reading for the mass as "m2".
- The difference between the two masses is the mass of the water which has vaporized (m=m2-m1).
- The energy supplied by the heater equals to the energy used to change water into steam
Pt=n Lv, from which Lv=P*t/m in (J/Kg).
- Some heat is lost to the surroundings and measured "m" is smaller than it should, thus the value of Lv obtained is greater than the true value.
-
Freezing
- What is the difference between melting and freezing?
the melting point is the same as the freezing point. An object absorbs heat to become
- What are the type of substances that have defined freezing points?
pure substances have fixed freezing points like pure water.
- How can we lower the melting point of ice?
- By increasing the pressure on the ice
- By adding impurities to the ice.
- For example salt reduces the temperature of melting ice to -18C
- Adding anti-freeze to car radiators in winter
- Spreading salt on icy roads
Boiling Point
- What is meant by boiling point?
When a liquid is heated, its temperature rises until it reaches the "boiling point" where it remains constant until all the liquid changes to vapor.
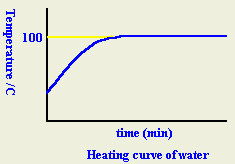
- What is meant by the "Latent heat of vaporization"?
Is the heat energy absorbed during boiling and changes liquid to vapor.
- Explain why the temperature the remains constant until all the liquid changes to vapor?
The latent heat of vaporization is the energy required to force the molecules far a part from each other to change the liquid into vapor. The molecules travel freely in random directions and their average kinetic energy dies not change which keeps the temperature constant during the change.
- What is meant by specific heat of vaporization?
It is the heat energy required to change one kilogram of the liquid into vapor state without any change in its temperature.
- What is the amount of heat absorbed during vaporization?
E=mLv
-
|