| 3 |
Properties
of Waves
|
Where to go! |
| 3.2 |
Light
|
|
B
|
Refraction of Light
|
Related Questions |
| Core-1 |
Describe an experimental
demonstration of the refraction of light |
|
| Core-2 |
Use the terminology for the
angle of incidence "i" and angle of refraction "r" and
describe the passage of light through parallel-sided transparent material |
|
| Core-3 |
give the meaning of the
critical angle |
|
| Core-4 |
Describe internal and total
internal reflection |
|
| Sup-1 |
Use the definition of
refractive index "n" in terms of speed |
|
| Sup-2 |
recall and use the equation n=sin(i)/sin(r) |
|
| Sup-3 |
Describe the action of optical
fibers |
|
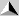 Refraction of
light Refraction of
light
- What is meant by refraction of light?
When a ray of light passes from one medium to another, it
bends. This bending of light is called "refraction".

- What is meant by "highly dense medium"?
If light travels slower in a medium than another medium, then
this medium is described as " highly dense medium" than the other.
- What is meant by "less dense medium"?
If light travels faster in a medium than another medium, then
this medium is called less denser than the other
- How lights bends when light moves from medium to
another?
When a ray of light enters a denser medium, it is bent towards
the normal.
When a ray of light enters a less dense medium, it is bent away from the
normal.
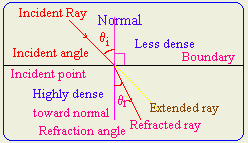
- Show when a ray of light enters a denser medium,
it is bent towards the normal.
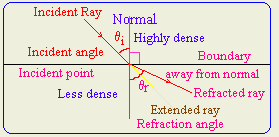
- Show when a ray of light enters a less dense
medium, it is bent away from the normal.
- What is meant by index of refraction?
There is an index of refraction
(n) is defined as the speed of light in vacuum divided by the speed of light in
medium.
- Define the followings: incident angle,
refraction angle, incident ray, reflected light, Normal?
incident angle the
angle between normal and incident ray
refraction angle the
angle between normal and refracted ray
incident ray the light ray that is
coming from light source and strikes the boundary surface.
reflected light the light ray that
emerges from the second medium
Normal the perpendicular line on the
boundary surface.
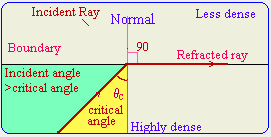
- What is meant by critical angle?
The critical
angle is the angle of incidence for which the
refracted ray is at 90 degrees with the normal.
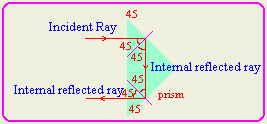
- What is meant by internal reflection and total
internal reflection of light?
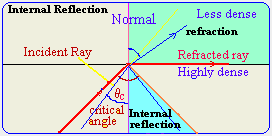
Internal reflection occurs
when the incident angle is equal to or less than the critical angle where
some of the light ray will be internally reflected and some refracted.
| The green region shows the the
refracted light area . The cyan region represented the reflected light
are.
|
|
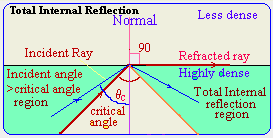
Total internal reflection occurs
occurs when the incident angle is always greater than the critical angle
where all light ray will be internally reflected.
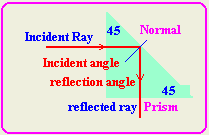
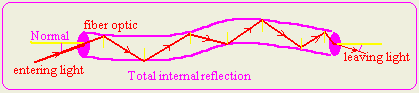
List two applications in ourlives which uses the concept of critical angle
and the total internal reflection.
1- Cameras: Cameras uses prisms to reflect light instead of mirror.
2- Fiber optics: Fiber optic are thin, flexible glass rods used to carry
light. The light enters the fiber optics at angle greater than the
critical angle of the fiber. In side the fiber light is totally reflected
from one side to the other until it leaves the fiber from the other end.
|


