| 2 |
Thermal Physics
|
Where to go! |
| 2.3 |
Transfer of Thermal Energy
|
|
D
|
Consequences of Energy Transfer
|
|
| Core-1 |
Identify and explain some of the everyday applications and consequences of conduction, convention and radiation |
|
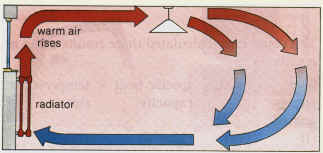
- Explain convection of air by heat radiators.
Most of the heat from a radiator is circulated by convection. Warm air around the radiator rises above the radiator and cooler air replaces it. The cooler air gets heated by the radiator and it rises and cooler air moves in to replace it. This process continues until all the air in the room has the same temperature.
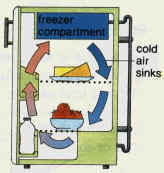
- Explain convection of air in refrigerators.
In a refrigerator, the freezer cools the air around it. As a result, the cooled air moves down and hot air at the bottom of the refrigerator moves up. This process continues until all the air in the refrigerator has the same temperature.
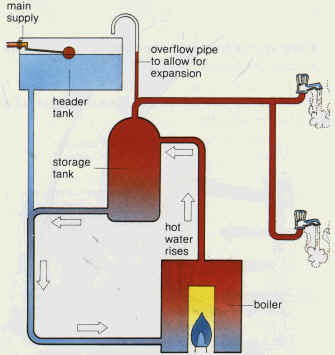
- Explain convection of water in hot-water supply system.
From the figure shown, water is heated in the boiler. It rises to the storage tank. Cooler water flows in to replace it. It too is heated. In time, a supply of hot water collects in the tank from the top down. The header tank provides the pressure to push hot water out of the raps.
|
 |
Explain why the freezer compartment in a refrigerator is placed at the top.
Because warm always rises and cooler air sinks. When warm air rises, it enters the freezer compartment and gets cooler and as a result it sinks and a new hot air rises. In time, all the air will be cooled.
Explain why a refrigerator does not work properly if the food is too tightly packed inside.
Because a tightly packed food will prevent the circulation of warm and cool air.
Explain why a radiator quickly warms all the air in a room, even though air is a very poor conductor of heat.
Because heat is carried due to the air circulations by convection rather than by conduction.
Explain why warm water rises when surrounded by cooler water.
Because it density is less than density of the cooler water surrounding it.
Explain how can we reduce heat lost due to convection?
This can be done by preventing air circulations. For example, when we cover hot tea we prevent air circulations and thus prevent convection to take place.

 Why vacuum flasks are made if double-walled glass vessels with vacuum between the walls and the walls are silvered?
Why vacuum flasks are made if double-walled glass vessels with vacuum between the walls and the walls are silvered?
They are made of double-walled glass with vacuum in between to prevent heat transfer from or to the liquid inside them. They are silvered because a silvered surface reflects heat radiation.

Why Greenhouses are made of glass walled rooms to keep warm climate in cold nights?
Because glass will prevent convection between the air trapped in rooms and the air outside rooms at the same time it allows heat radiation to enter from glass which supply heat to the insides of the room. During cool night, the heat energy gained from radiation is emitted back inside the house which keeps warm during the night.
 Why cloudy nights remain warm?
Why cloudy nights remain warm?
When air rises up it cools down and becomes more dense. Thus it sinks down until it reaches the Earth surface which in return cools the surface. When cloud are present, they prevent cool air to sink and reach the surface. Also, the reflect heat radiations and prevent them from reaching ground.
Why people wear dark clothes in winter and white clothes in summer?
People wear dark clothes in winter to keep warm because dark cloths are good absorbers of heat radiations. On the other hand, people wear white clothes in summer to keep cool because white cloths are good reflectors of heat radiations.

|




