Cooling Curve
|
|
Objective
|
To enable the student to study the cooling curve of a given material |
|
Theory
|
A hot body loses its energy gradually to the surroundings in time. By measuring the body temperature as it drops with time, we can plot the temperature and get its cooling curve. The temperature will continue dropping until it reaches the room temperature as shown in the illustrative curve below.
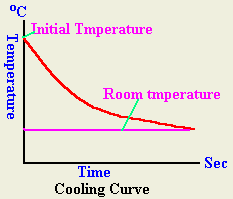
The rate of cooling of a body depends upon differences in temperature between the body and surroundings, the exposed area of the body and the nature of the radiation surface. For example, a block body is a good radiator. |
| Tools |
- Container: to hold the hot water
- Water: to plot it cooling curve
- Lagging: to prevent heat from being lost to the surroundings
- Thermometer: to measure temperature
|
| Equipment |
- Stop-watch: to measure time interval during which heat is lost and temperature is measured
-
|
| Precautions |
Thermometer Precautions
- The mercury thread should be kept along the scale to avoid error due to parallax
- line of sight should be perpendicular to scale
- Reading should be at the top of mercury thread
|