|
Cathode Ray
- What meant by a cathode ray?
A cathode ray is a beam of fast-moving
electrons.
- Why it is called cathode ray?
Because it emerges from the cathode
- What is meant by thermionic
emission?
It is the break up of electrons off metals into the space
surrounding them due to the gained energy from heat.
- Explain the structure of a cathode ray tube?
The tube is made of glass with all air
removed from it. Inside the glass there are two pieces of metal called
electrodes. One of these is called the anode and the other is called
the cathode.
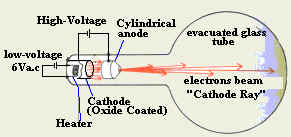
- Why the air is removed from the glass tube?
It is removed so that the electrons are
free to move without colliding with air molecules
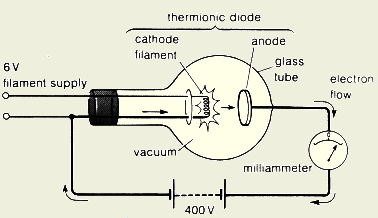
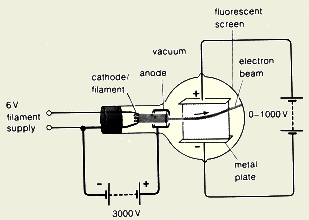
- Explain how do we generate cathode
ray?
We connect the filament of the cathode to a
suitable power supply and we connect the anode to the positive terminal of a
high voltage power supply as shown below. When the filament heats the
cathode, the electrons start to gain energy and escape from the cathode
surface. Electrons leaving the cathode are accelerated toward the
anode due to the high potential and the positive charge on the anode.
The accelerated electrons form a fast-moving beam of electrons called
"cathode ray".
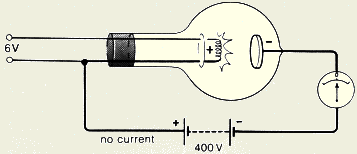
- Explain why current does not flow in the circuit
shown?
In the circuit below, the anode has a negative charge and thus it
will not attract the escaped electrons. As a result no current will be
detected by the ammeter shown in the circuit.
- List the basic properties of cathode ray?
- Travel in straight lines
- A beam of negatively charged particles
- Can be deflected by electric field
- Can be deflected by magnetic field
- Produce fluorescence (glow) when they hit some materials.
This property is used to design screens for TVs, computers,
oscilloscopes, ..etc.
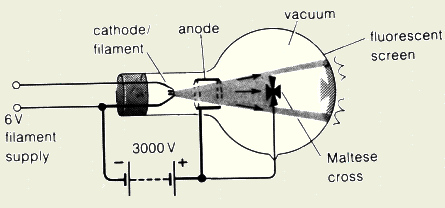
- Explain an experiment to show that cathode ray
travels in straight lines?
As shown in figure below, we put an object like the Maltese cross.
When the cathode ray accelerates toward the screen part of it will be
blocked by the cross and the other part is reach the screen. On the
screen, we see an image exactly proportional to the cross, which indicate
that electrons must have traveled in straight lines.
- Explain an experiment to show that cathode ray
can be deflected by electric field?
The circuit below shows that when the cathode ray enters the electric
filed set by the two plates it is deflected toward the positive
terminal. This happens because the positive charge on the top plate as
shown attracts the electrons.
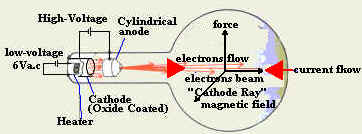
- Explain an experiment to show that cathode ray
can be deflected by magnetic field?
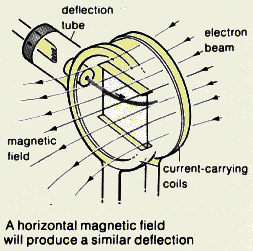 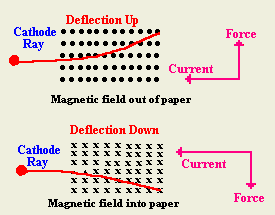
- Explain an experiment to show that cathode ray is
made of negatively charged particles?
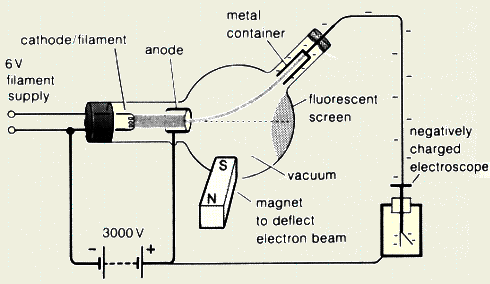
- Show the difference between the
direction of flow of electron current and conventional current
for the cathode ray?
-
|