|
Effect of forces
- What might happen to an object when a force act upon it?
- Accelerate or decelerate
- Change direction
- Rotate the object
- Change its shape and size
- increase its momentum
- How a force may change the motion of a body?
A force may change the speed or the direction or both.
- To change the speed only, we apply a force in the direction of motion.
- To change the direction only, we apply a force that is perpendicular
to the direction of motion
-
Turning Effect of forces
- What will happen to an object that is
hinged at one point and force is applied at any point a way from the hinged
point?

the object will rotate around the hinged point and the applied force is
called the "turning force".
The hinged point is called the "pivot"
or the "fulcrum".
- What is meant by "the line of action of a
force"?
Is the extension of the force vector
- What are the factors that determine the size of
the turning effect?
1- the magnitude of the force
2- the distance from the the line of action of the force from the pivot.
- What is the definition of moment?
Moment is the turning effect of a force about a pivot and it is
defined as
Moment=force*perpendicular distance from the pivot.
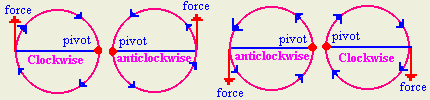
- Classify moments based on direction.
Clockwise moment: is the
moment resulted by a force that turns the object around the pivot in the
same clockwise direction.
Anticlockwise moment: is the moment
resulted by a force that turns the object around the pivot in the opposite
direction to the clockwise direction.
- How do we determine the direction of moment?
- Define equilibrium?
A system is said to be in equilibrium if it is not rotating on
point in the system and the net forces acting on the system is zero.
- What are the equilibrium conditions?
- The sum of all forces in one direction is equal to the sum of all
forces in the other direction.
- The sum of all clockwise moments is equal to the sum of all
anticlockwise moments at any point in the system.
- State the principle of moments?
The sum of all clockwise moments is equal to the sum of all
anticlockwise moments at any point in the system.
- What is meant by the support force?
Is the force provided by the support to hold the system in equilibrium
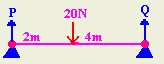
- In the diagram shown, calculate the support
forces at P and Q.
- In the diagram shown, Calculate P which will make
the system in equilibrium.
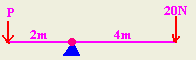
Effect of force on shape and size
- What is meant be "extension"?
- Explain the extension/load graph.
- Define the followings:
- elastic limit
- elastic material
- linearly proportional
- none linearly proportional
- States Hooke's Law
- In a spring stretching experiment, the following readings were obtained.
- What is the unstreched length of the spring?
- Plot the data
- Mark the elastic limit
- Mark the Hooke's law region.
|