| 3 |
Properties
of Waves
|
Where to go! |
| 3.3 |
Sound
|
|
| Core-1 |
Describe the production of
sound by vibrating sources |
|
| Core-2 |
Describe the longitudinal
nature of sound waves |
|
| Core-3 |
State the approximate range of
audible frequencies |
|
| Core-4 |
Show an understanding that a
medium is required to in order to transmit sound waves |
|
| Core-5 |
Describe an experiment to
determine the speed of sound in air |
|
| Core-6 |
Relate the loudness and pitch
of sound waves to amplitude and frequency |
|
| Core-7 |
Describe how the reflection of
sound may produce an echo |
|
| Sup-1 |
Describe compression and rarefaction |
|
| Sup-2 |
State the order of magnitude of
the speed of sound in air, liquids, and solids |
|
Sound
- Describe how sound is produced?
Sound is produced by vibrating an object into its surrounding
medium. The vibration produces compressions and rarefactions in the surrounding
medium resulting in longitudinal waves. When compressions and
rarefactions reach the ear drum, they result in the sensation of sound
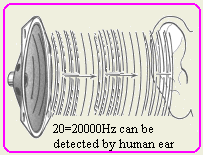
provided that the frequency of the waves is between 20-20000Hz.
- Describe the longitudinal nature of sound?
Sound produces longitudinal waves which cause vibrations in the
medium in the direction of the traveling wave.
- What is the approximate range of audible sound?
Audible sound has a frequency between 20-20000HZ
- What is meant by infrasonic?
Sound waves with frequency below 20Hz are called infrasonic sound
waves
- What is meant by ultrasonic?
Sound waves with frequency above 20000Hz are called ultrasonic
sound waves
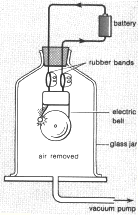
- Describe an experiment to show that sound
requires a medium to be transmitted?
| Equipment: 1-electric bell, 2- glass jar,
3- vacuum pump, 4-power source
By removing the air from the jar, it is possible to show that sound
cannot travel through vacuum. |
 |
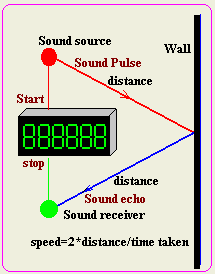
Describe an experiment to determine the speed of
sound.
| We take a sound source and produce a pulse
of sound from the source as shows by the red spot. During that the
timer receives a starting signal to start counting time The
sound wave will ravel and strikes the wall. It will be reflected
off the wall and then be detected by the sound receiver, which will
send a stop signal to the timer.
The sound traveled the double the distance and therefore its speed
is given by
speed=2*distance/time taken. |
 |
What is meant by the followings terms?
intensity: is the power
carried by the wave through a unit of area erected perpendicular to the
direction of propagation.
Loudness: is a term used to measure the
human perception of sound
Pitch: is the timbre, quality of sound,
tone, or sharpness.
What is the relation between frequency, amplitude, pressure, temperature and loudness, pitch, intensity, speed.
| Parameter |
Frequency |
Amplitude |
Pressure |
Temperature |
| loudness |
independent |
directly |
independent |
independent |
| pitch |
directly |
independent |
independent |
independent |
| intensity |
directly2 |
directly2 |
independent |
directly |
| speed |
independent |
independent |
independent |
directly |
What are the factors which the intensity of sound
depends on?
frequency square, speed, amplitude square, medium density.
Where I=2vrp2f2A2
where is r: density (kg/m3)
f: frequency (Hz)
A: Amplitude (m)
v: speed (m/s)
Describe how the reflection of sound may produce
echo?
Sound echoes are sound waves reflected off large objects.
They are heard after a short time of the original sound because the
reflected wave needs time to bounce off objects and reach the observer.
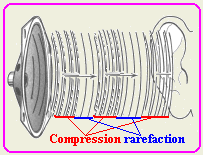
Describe compression and rarefaction?
| When the speaker cone is pushed toward the
ear, it compresses the air as shown. When the speaker cone is
pulled a way from the ear, it stretches the air resulting in
rarefaction. The series of compressions and rarefactions are
traveling through air until it reaches the ear drum. |
 |
Compare between sound speed in liquids, gases,
and solids?
330m/s in air, 1400 m/s in water, and 5000 m/s in solids.
|