| 3 |
Properties
of Waves
|
Where to go! |
| 3.2 |
Light
|
|
C
|
Thin Converging Lenses
|
Related Questions |
| Core-1 |
Describe the action of a thin
converging lens on a beam of light |
|
| Core-2 |
Use the term focal length |
|
| Core-3 |
Draw ray diagram to illustrate
the formation of a real image by a single lens |
|
| Sup-1 |
Draw ray diagram to illustrate
the formation of a virtual image by a single lens |
|
| Sup-2 |
Use and describe the use of a
single lens as a magnifying glass. |
|
Lenses
- What are the main two types of lenses?
Convex and Concave lenses
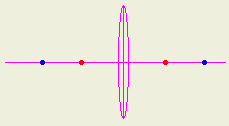
- What is meant by the principle focus of a convex lens?
The principle focus of a convex lens is the point at the axis
that passes through the optical center of the lens and where the incident
rays parallel to the axis are refracted passing through it.
- What is meant by the principal focus of a concave lens?
The principal focus of a concave lens is the point at the
principle axis that passes through the optical center of the lens and where
the incident rays parallel to the axis are refracted so that their
extensions pass through it.
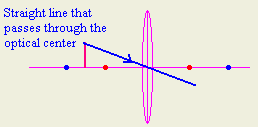
- What is meant by the principal axis lens?
Is a straight line that passes through the
optical center and the focus of the lens
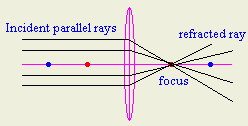
- How could you find the focal length of convex
lens rapidly?
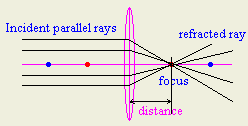
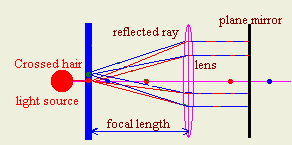
- How could you find the focal length of convex lens accurately?
- How could you distinguish by structure between a convex lens and concave
lens?
Convex lenses are thick in the middle while concave lens are thin
in the middle
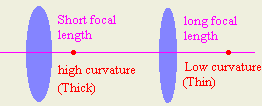
- What is the relation between the focal length and the curvature of a lens?
inverse relation
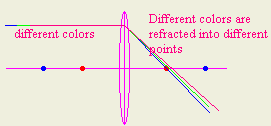
- Give two reasons why in practice a convex lens may not bring parallel rays
to an exact point focus.
1- Convex lenses refract light of different colors by slightly
different amount. So they will not converge in one point
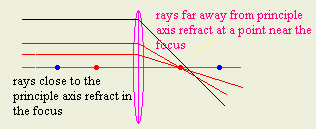
2- Convex lens converge parallel ray in one point if and only if they are
very close to the principle axis.
- Explain how do we draw the image of an object placed in front of a convex
lens?
1- Draw a straight ray from the top most point in the object that
passes through the optical center.
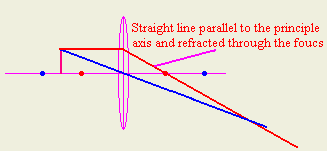
2- Draw a straight ray from the most top point in the object parallel to the
principle axis and then refract it so it passes in the focus
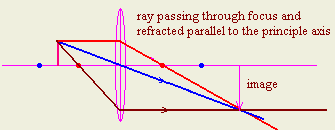
3- Draw a straight ray passing in the focus and refract it parallel to the
principle axis
- Explain how do we draw the image of an object placed in front of a concave
lens?
>
- An object is placed beyond the focal length of a convex lens. Draw a
ray diagram to show how the image is formed and describe the image nature?
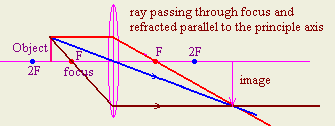
- An object is moved from beyond the focal length of a convex lens toward
its optical center, what effect will occur on the image size, and position?
- State where an object should be placed if the image formed by a convex
lens is to be:
a- large, upright, and virtual. u<F
b- real and smaller than the object. u>2F
c- real and larger than the object. 2F>u>F
d- real and the same size as the object.
u=2F
e- real and at the minimum possible distance from the object.
u=F
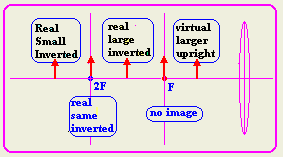
- What is the minimum possible distance between an object and its image
under a convex lens. It is 4 times the focal length.
- Describe the lenses formula and the magnification factor.
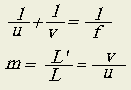
u: distance between object and optical center
v: distance between image and optical center
+ (positive) real image, inverted
- (negative) virtual image and upright
f: focal length.
+ (positive) for convex lenses
- (negative) for concave lenses
L': image length
L: object length
m: magnification
- Define "real image" and "virtual
image"?
Real image is an image that can be put on
screen
Virtual image is an image that cannot be put on screen.
-
Problems
- A 3cm high object is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length
8 cm. Calculate the position, height and nature of of the
image.
given:
L=3cm, u=24 cm, f=+8 cm
required: v?, L'?, image properties?
Solution:
1/u+1.v=1/f , 1/24+1/v=1/8,
1/v=1/8-1/24=2/24=1/12, v=12 cm
m=L'/L=v/u, L'/3=12/24, L'=1.5 cm
image: real, inverted, smaller
- A 3cm high object is placed 3 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8
cm. Calculate the position, height and nature of of the
image.
given
given:
L=3cm, u=3 cm, f=+8 cm
required: v?, L'?, image properties?
Solution:
1/u+1.v=1/f , 1/3+1/v=1/8,
1/v=1/8-1/3=-5/24=1/12, v= -24/5= - 4.8 cm
m=L'/L=v/u, L'/3=4.8/3, L'=4.8 cm
image: virtual, upright , larger
-
-
-
|